Now that Microsoft has released SQL Server for Linux, even if your main tech stack is tied to a Windows Server you may want to copy the database to another SQL Server located on a Linux computer. This can come in handy, for example, if you wanted to provide developers with a database for testing without buying a Windows Server license.
There are a few ways to tackle this task. This article examines the following methods to copy the SQL Server database from Windows to Linux:
- Using T-SQL’s BACKUP DATABASE and RESTORE DATABASE commands
- Generation of T-SQL database script (such as mysqldump)
- Creating BACPAC
- SqlBak service
Below you will find a summary of each method.
Using T-SQL’s BACKUP DATABASE and RESTORE DATABASE commands
For this first method, you’ll create a native backup and facilitate its restoration to an SQL Server located on the Linux server.
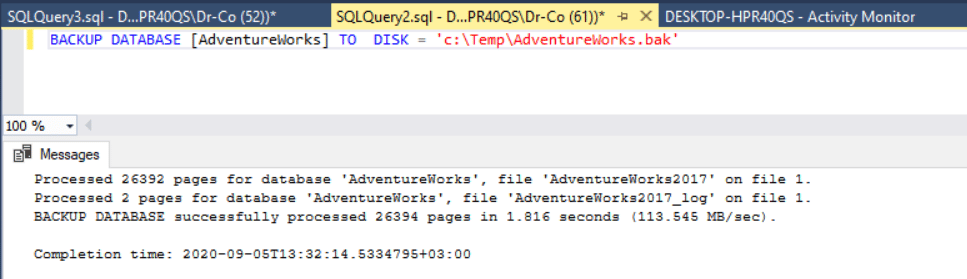
First, run BACKUP DATABASE command on the Windows server:
BACKUP DATABASE [AdventureWorks] TO DISK = 'c:\Temp\AdventureWorks.bak'
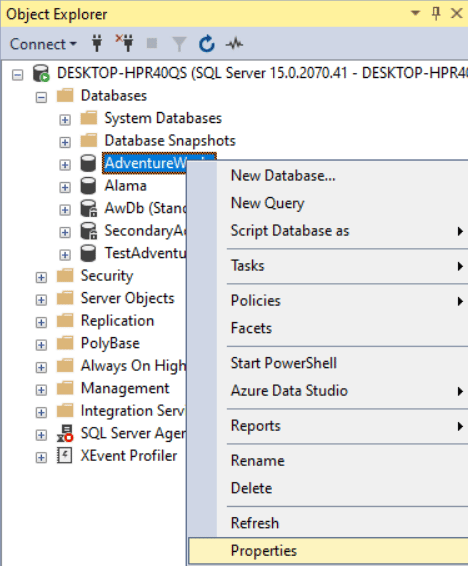
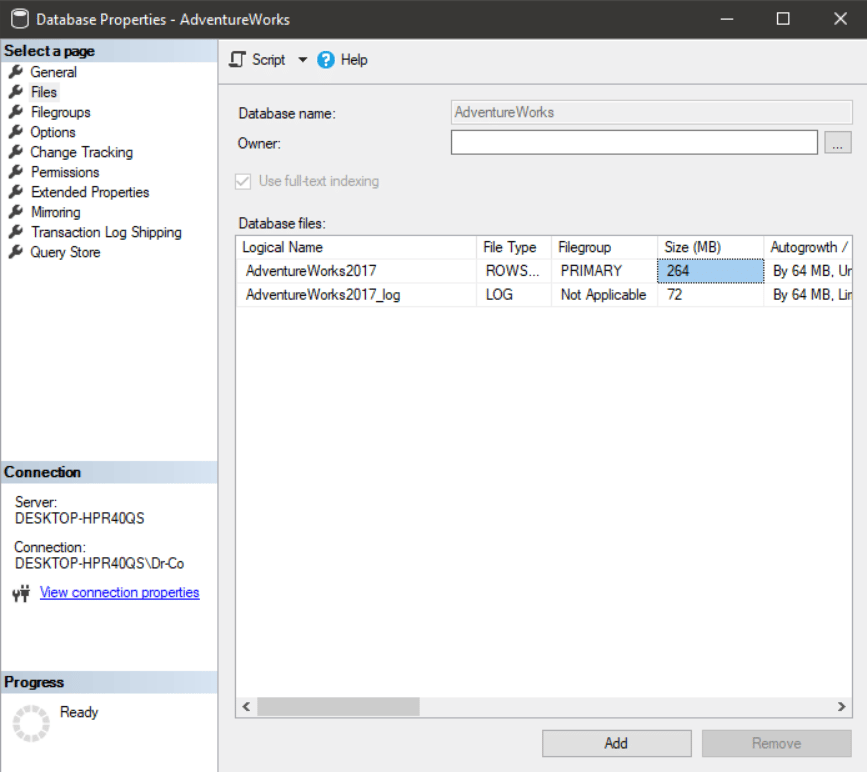
We also need to know the logical names of database files to restore a database on a Linux server. These can be viewed in SSMS by right-clicking on the database and selecting “Properties.”
In the window that appears, select “Files,” and the Logical Name column will contain a list of database file names.
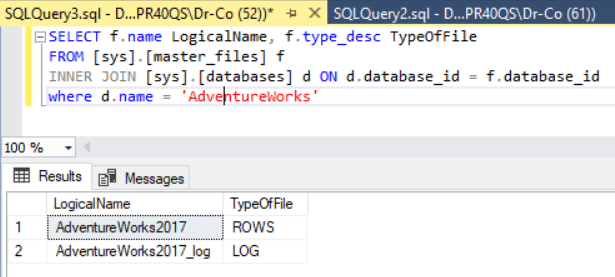
You can also get the database file names through the following T-SQL query:
SELECT
f.name LogicalName,
f.type_desc TypeOfFile
FROM [sys].[master_files] f INNER JOIN [sys].[databases] d ON d.database_id = f.database_id
WHERE d.name = 'AdventureWorks'
After you have made a backup and found out the database file names, it’s time to restore it on Linux. First, you need to copy the backup file to the Linux server, and then you can restore the database.
You will need to specify the path in RESTORE DATABASE command not only to the location of the copied backup but also to the files in which the database will be physically stored. We learned the names of these files during the previous step.
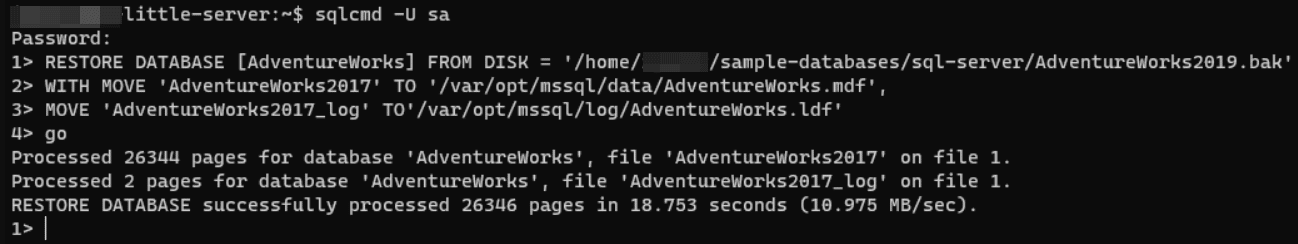
RESTORE DATABASE [AdventureWorks]
FROM DISK = '/home/username/AdventureWorks.bak'
WITH MOVE 'AdventureWorks2017' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/AdventureWorks.mdf',
MOVE 'AdventureWorks2017_log' TO '/var/opt/mssql/log/AdventureWorks.ldf'
You can execute a T-SQL query on a Linux server using sqlcmd utility or SSMS if remote connections are allowed. Executing BACKUP DATABASE and RESTORE DATABASE commands are a good way to move a database from Windows to Linux.
Problems can arise if the source and target SQL server have different versions.
Generate T-SQL script
Another way to move a database from a Windows server to a Linux server is to create a T-SQL script. This is similar to what mysqldump or pg_dump does.
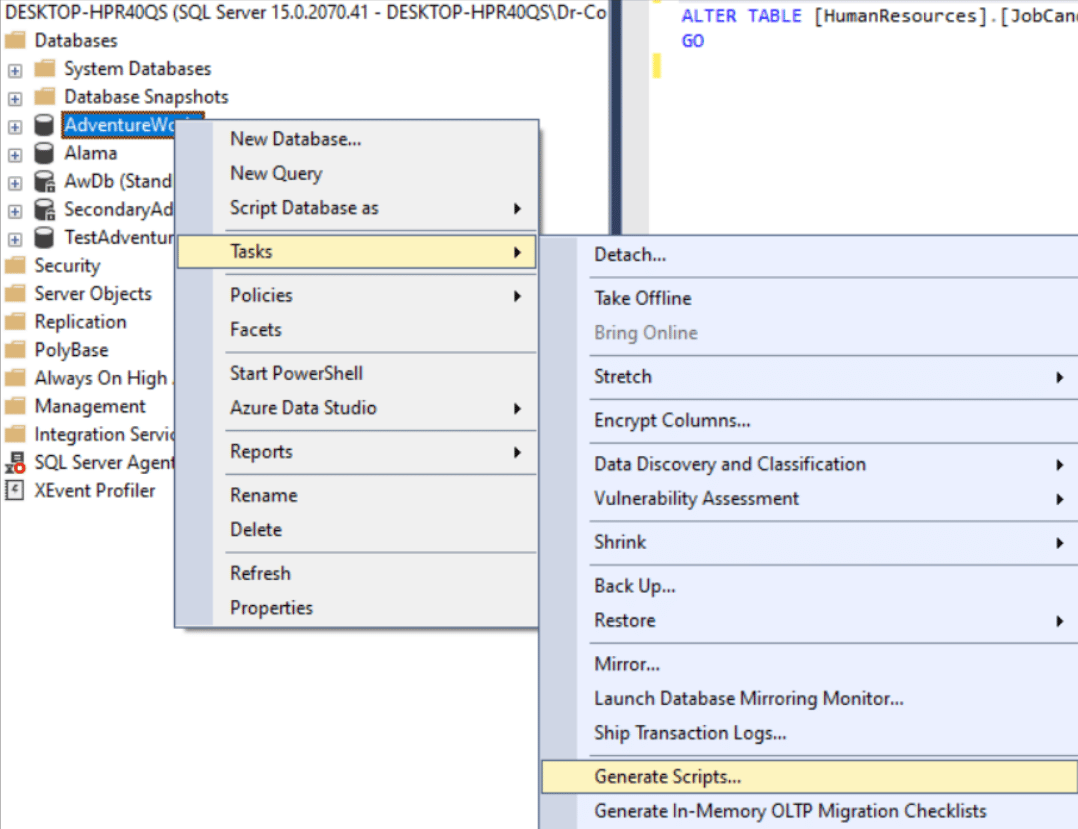
You can create a script with SSMS.
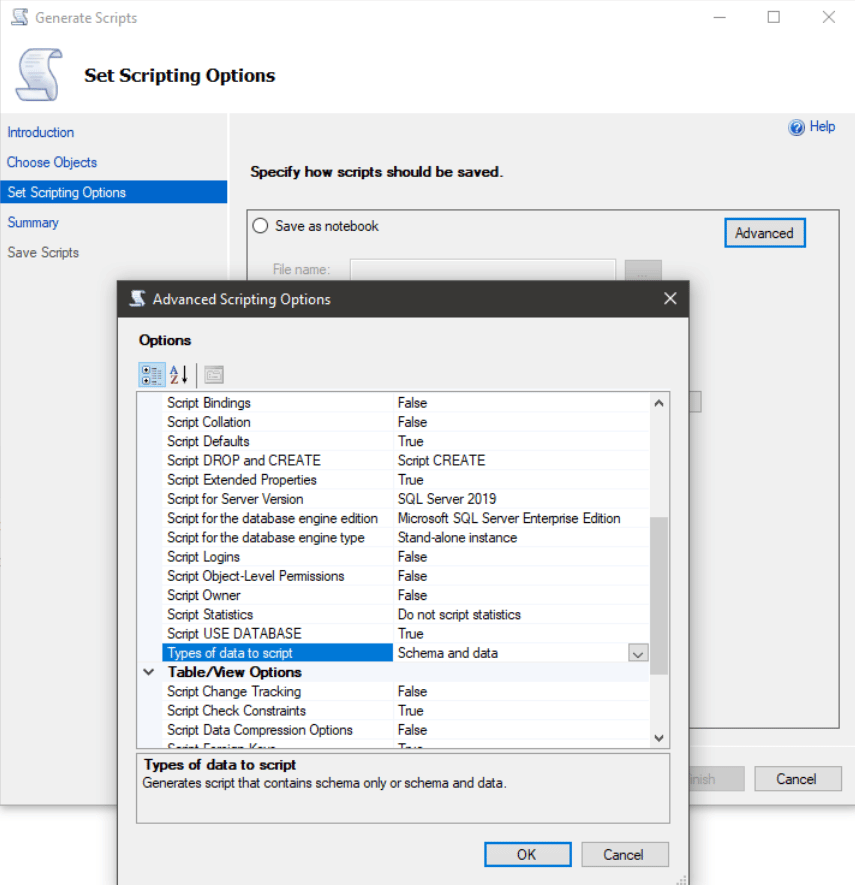
The wizard will launch. Here, in addition to specifying the Output file, you will need to specify both Schema and Data as types of data to submit. Only Schema is selected by default.
In the created .sql file, replace the paths to .ldf and .mdf files with those that are supported in Linux:
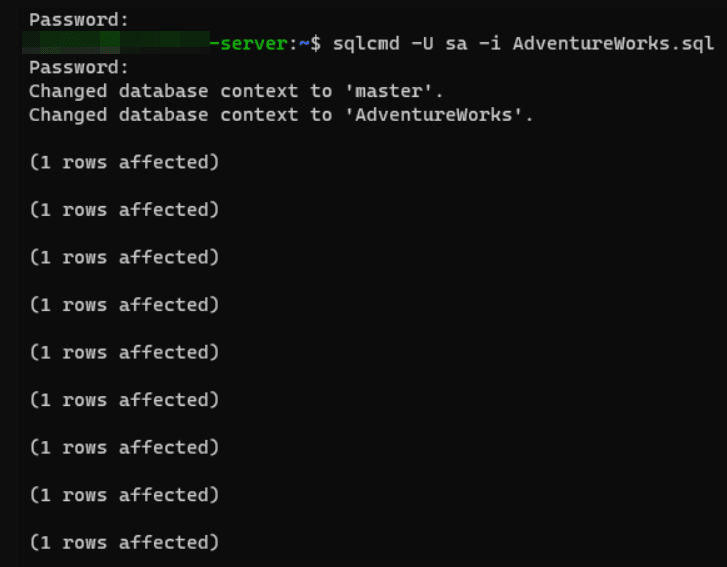
To import a .sql file, you can use sqlcmd utility by submitting a file with a script using the -i parameter.
sqlcmd -U SA -I AdventureWorks.sql
Creating a script on a Windows server and then executing it on a Linux server is a good solution. It is convenient to work with a .sql file because before importing it, you can view it and change something if necessary. However, as in the case with BACPAC, when exporting, it is desirable to create a snapshot to export data in a consistent state.
The main disadvantage of this method is the large file size, and a long time required to create, and especially to import, data.
Export\Import Data-Tier application
The database can be packed into a BACPAC file. It is a file that encapsulates a database’s schema and data. BACPAC is used to migrate a database from one server to another.
On Windows, BACPAC export can be done in two different ways:
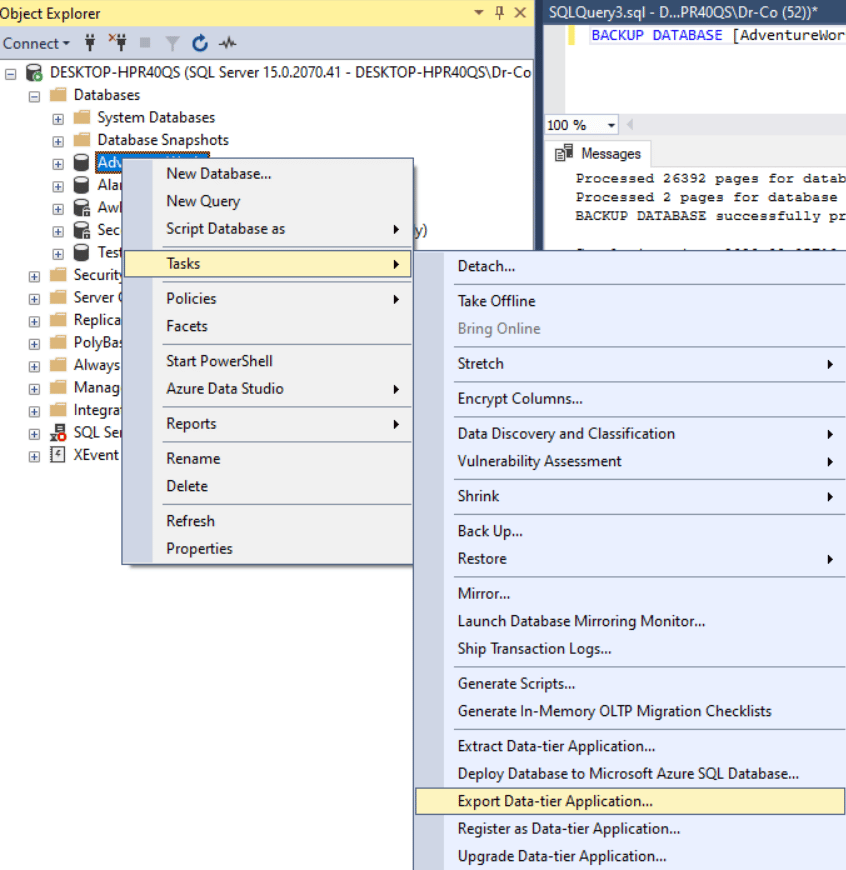
Via SSMS
Select Export Data-Tier Application to export.
The export wizard will start, where you need to specify the name and path of the .bacpac file.
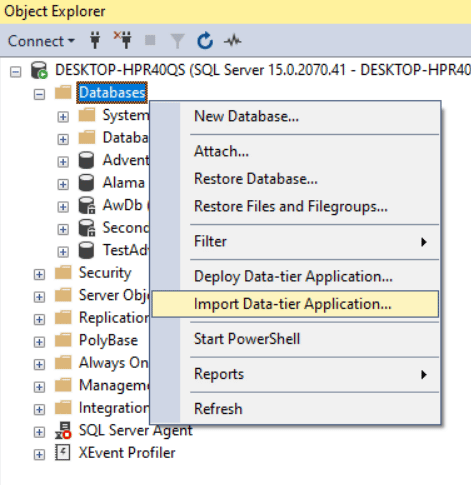
If you can connect using SSMS to SQL server installed on Linux, then you can import the database via SSMS.
Select Import Data-Tier Application to import.
Via SqlPackage
You can create a BACPAC and import it not only via SSMS. Another way to create a BACPAC is to use the SqlPackage utility.
SqlPackage is a utility that can help you migrate data between different SQL Servers. More information about it can be found here and you can download it for Linux and Windows here.
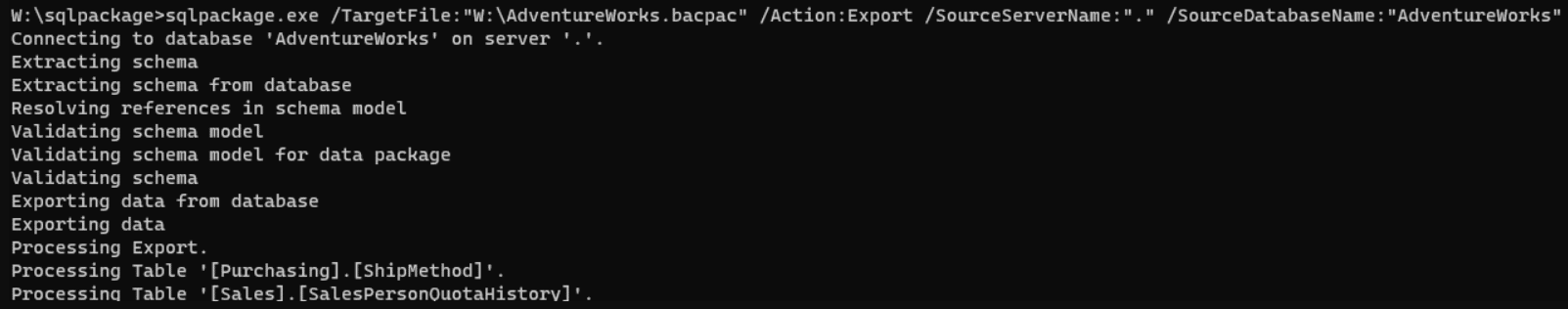
To create a BACPAC via sqlpackage, you need to run the command in the command line:
sqlpackage.exe /TargetFile:"W:\AdventureWorks.bacpac" /Action:Export /SourceServerName:". " /SourceDatabaseName:"AdventureWorks"
Run the following command to import:
sqlpackage /a:import /SourceFile:AdventureWorks.bacpac /TargetDatabaseName:"AdventureWorks" /TargetServerName:. /TargetUser:sa /TargetPassword:<your passsword>
Export/Import Data-tier Application is convenient in that you do not need to have access to the file system of the servers you are working with. Also, as a rule, the BACPAC file is smaller in terms of size than the .bak file, and also exported and imported faster than .sql script.
However, this method has a serious drawback. When creating a BACPAC of a live database – it may turn out to be inconsistent in terms of transactions. Therefore, before exporting BACPAC, it is advisable to either switch the database to read-only mode or create a snapshot of the source database and export the snapshot.
SqlBak
If you need to copy the SQL Server database regularly, such as to create a test environment, Sqlbak can help you with it.
SqlBak is a service for creating backups and sending them to cloud storage. In addition, it can restore after a backup on another server.
First, you need to register and install SqlBak service on Windows and Linux servers, and also configure connections to the SQL Server there. Details can be found here.
Then create a backup job on the server, from which you want to copy a database.
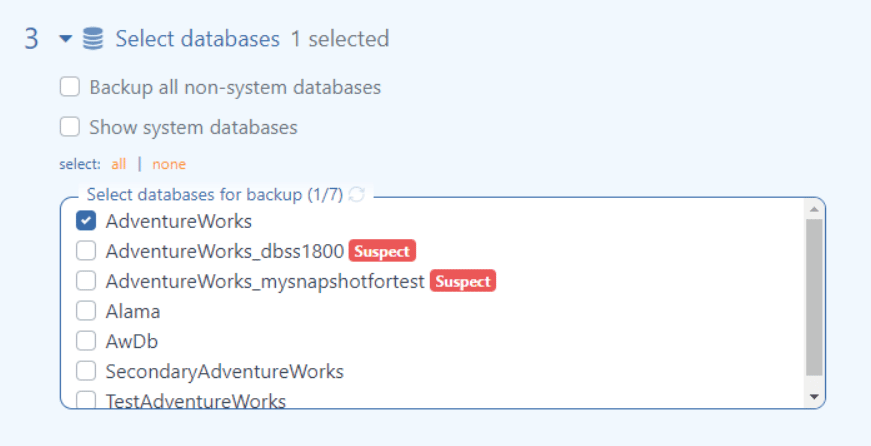
A new job window will pop up. From that window, select the database you want to move to Linux.
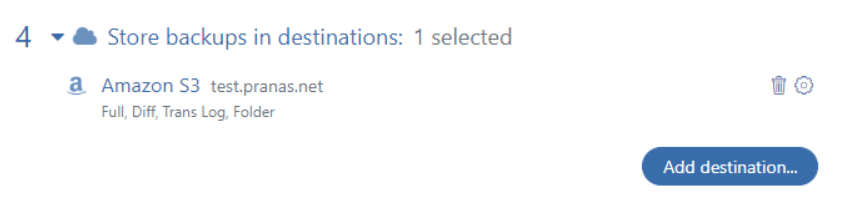
Then select the destination to which the backups will be moved (for example S3).
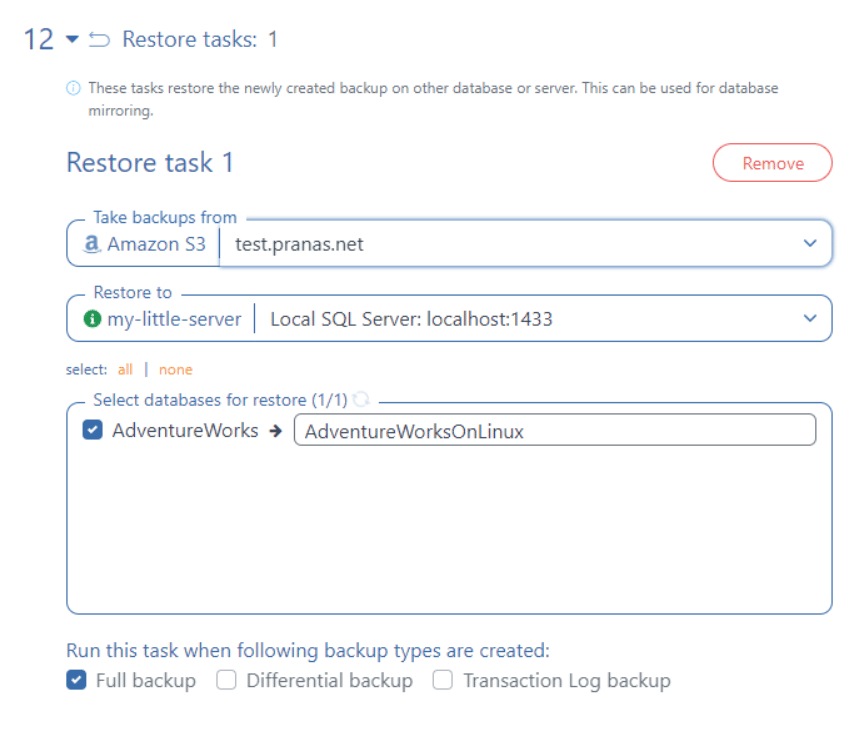
Finally, you can configure the restore task launch on another server.
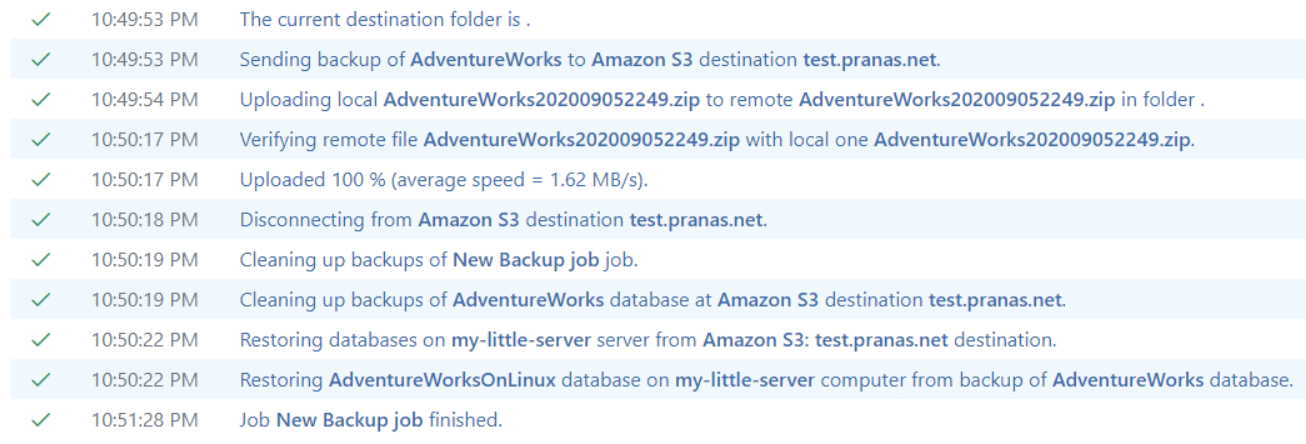
After that, you can save and start the job to make sure that everything works correctly. At the end of the job log, there will be a restore task record on the Linux server.
The main advantage of SqlBak is the automation of the copy process. SqlBak allows you to schedule regular jobs, and email notifications can be configured in the event of failure.
SqlBak also supports Differential and Transactional log backups, which are much smaller and faster to create. This may come in handy for regular database cloning.
Bottom Line
Therefore, to migrate an SQL Server from Windows server to Linux, you just need to perform a backup on Windows and restore it on Linux. Backup can be done in different ways. Sometimes it’s easier to do it through native SQL Server backup, and sometimes it’s easier to create a .bacpac or .sql script.
If you need to regularly clone a server, then it is better to use third-party services such as SqlBak, which will handle file transfer and notify you in the event of failure.